Cognitive Behavioral Therapy vs. Dialectical Behavior Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) are both evidence-based psychotherapies used to treat a variety of mental health conditions. While they share similarities, they differ in focus, techniques, and the types of conditions they target.
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Core Principle:
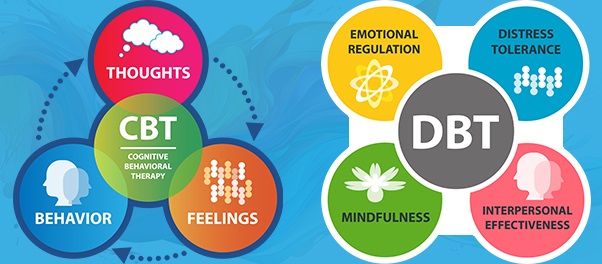
CBT is based on the idea that thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected. By identifying and changing negative or distorted thinking patterns, individuals can alter their emotional responses and behaviors.
Key Features:
- Focus: Emphasizes identifying and challenging distorted cognitive patterns (e.g., negative or irrational thoughts) and replacing them with more realistic, positive thoughts.
- Techniques: Cognitive restructuring, thought records, behavioral experiments, exposure therapy, and problem-solving strategies.
- Commonly Used For: Depression, anxiety, PTSD, phobias, OCD, and general stress management.
- Structure: Goal-oriented and typically short-term. Sessions are structured, with homework assignments between sessions to reinforce learning.
- Key Concept: Cognitive distortions (irrational thought patterns like catastrophizing or black-and-white thinking).
2. Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
Core Principle:
DBT builds upon CBT but integrates concepts of mindfulness and acceptance from Eastern philosophies. It focuses on balancing acceptance of one’s experience with the need for change.
Key Features:
- Focus: DBT emphasizes emotion regulation, distress tolerance, mindfulness, and interpersonal effectiveness. It aims to help people manage intense emotions and improve relationships.
- Techniques: Mindfulness exercises, distress tolerance skills (like self-soothing), emotion regulation techniques, and interpersonal effectiveness training.
- Commonly Used For: Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD), suicidal ideation, self-harm, eating disorders, and substance abuse. It’s particularly effective for individuals who experience extreme emotional reactions or difficulty managing emotions.
- Structure: DBT includes individual therapy sessions, skills training groups, and sometimes phone coaching. It's often longer-term than CBT and has a strong emphasis on group work and skills acquisition.
- Key Concept: Dialectics—balancing acceptance (of where the person is emotionally) and change (the need for progress).
Main Differences
- Acceptance vs. Change: While both therapies focus on changing unhealthy thoughts and behaviors, DBT places a stronger emphasis on acceptance (of the present moment) as well as change. CBT tends to focus primarily on change.
- Skills Training: DBT includes a formal skills training component (mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness) that CBT does not.
- Emotional Regulation: DBT is more focused on emotional regulation, especially for individuals with intense emotional reactions, whereas CBT is broader and tackles general negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Target Populations: CBT is often used for mood and anxiety disorders, while DBT is more commonly used for complex conditions like BPD and issues involving emotional dysregulation.
In summary, CBT is more about restructuring thoughts and behaviors, while DBT incorporates mindfulness and acceptance strategies to help individuals cope with emotional intensity.



Comments
Post a Comment